High performance brushless linear motors are combined using linear motor magnets and coils.
Order(MOQ):
5Payment:
100% INADVANCEProduct Origin:
ChinaShipping Port:
Xiamen/Shanghai/NingboColor:
SliverLead Time:
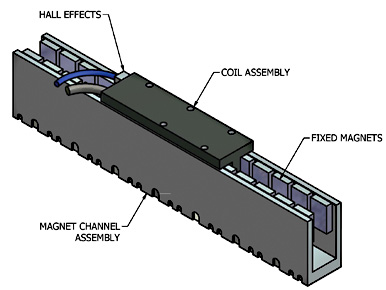
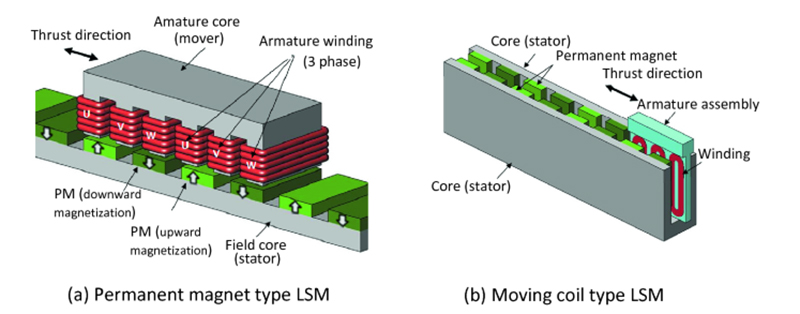
25-35 daysThe new linear electric motor design goes back to rotary ideas. The motor itself is contained within a nonmagnetic steel housing. A self-supporting coil sits inside, along with the sleeve bearing of the forcer rod made out of special slide-bearing material. The coils are glued and connected together and after the insertion in the housing a plastic injection makes for a self-supporting structure so that there is no core for the structure rigidity.
How to choose the right linear motor?
Linear motor selection specifications are mainly for the choice of thrust. In order to accurately select the thrust of the linear motor, it is necessary to know the load weight, effective stroke, maximum speed and maximum acceleration
Linear motor application:
(1) Material Handling.
(2) Pick and place machines.
(3) Component insertion, inspection and drilling.
(4) Medical examination.
(5) Laser cutting.
(6) Carpet tufting.
(7) Semiconductor.
(8) Lathes.
Advantages:
(1) Simple structure.
(2) Suitable for high-speed linear motion.
(3) High utilization rate of primary winding.
(4) No lateral edge effect.
(5) Easy to overcome the problem of unilateral magnetic pull.
(6) Easy to adjust and control.
(7) Strong adaptability.
(8) High acceleration.
Common problems:
Q: What is the difference between linear induction motor and traditional motor?
A: Linear induction motors achieve linear motion through induction principles, while traditional motors are driven by rotational motion.
Q: What is the control mode of linear induction motor?
A: The control mode of linear induction motor is usually closed-loop control, and accurate control is achieved through feedback system.
Q: What applications is this motor suitable for?
A: Linear induction motors are suitable for applications that require accurate, high-efficiency, low-noise linear motion, such as automation equipment, industrial machinery, and medical equipment.