NdFeB Countersunk Hole Magnet N45 Grade D25x5mm 14.5lb Pulling Force
These magnets come in various shapes and sizes, with the countersunk hole typically located on one of the flat surfaces of the magnet. They are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, engineering, electronics, and automotive, where they can be employed in applications such as magnetic closures, fixtures, displays, sensors, and more.
Brand:
KINGS MAGNETItem NO.:
C/S25-5NDOrder(MOQ):
10Payment:
T/T 100% IN ADVANCEProduct Origin:
CNShipping Port:
XIAMENColor:
SilveryLead Time:
25-35 DAYSWeight:
17NdFeB countersunk hole magnets, also known as neodymium countersunk magnets, are powerful magnets made from a combination of neodymium, iron, and boron (NdFeB). These magnets are known for their exceptional strength and are widely used in various applications where a strong magnetic field is required.
|
Product Code:C/S25-5ND |
|
|
|
|
|
No. |
Item |
Descriptions |
|
1 |
Size |
D25x5mm-d10/5 |
|
2 |
Density |
7.5 g/cm³ |
|
3 |
Vertical pull-off force |
14.5lb |
|
4 |
Magnetisation direction |
Axial |
|
5 |
Magnet Grade |
N45 |
|
6 |
Coated |
Ni-Cu-Ni |
|
7 |
Max. W.T. |
80C |
|
8 |
Gauss value |
2200gs |
|
|
|
|
Here's some key information about NdFeB magnets:
Composition: NdFeB magnets are composed mainly of neodymium (Nd), iron (Fe), and boron (B). The exact composition may vary depending on the specific grade of the magnet and its intended application.
Magnetic Properties: NdFeB magnets exhibit exceptionally strong magnetic properties, with high coercivity (resistance to demagnetization) and high remanence (ability to retain magnetization). They have the highest magnetic energy product of any material known, making them indispensable in various industrial and consumer applications.
|
Grade |
BrmT(KG) |
bHc KA/m(KOe) |
iHc KA/m(KOe) |
(BH)maxKJ/m3 (MGOe) |
Tw.℃ |
|
N35 |
1170-1220(11.7-12.2) |
≥868( ≥10.9) |
≥955(≥12) |
263-287(33-36) |
80℃ |
|
N38 |
1220-1250(12.2_12.5) |
≥899( ≥11.3) |
≥955 ( ≥12) |
287-310(36-39) |
80℃ |
|
N40 |
1250-1280 (12.5-12.8) |
≥907 ( ≥11.4) |
≥955 ( ≥12) |
302-326(38-41) |
80℃ |
|
N42 |
1280-1320(12.8-13.2) |
≥915( ≥11.5) |
≥955 ( ≥12) |
318-342(40-43) |
80℃ |
|
N45 |
1320-1380(13.2-13.8) |
≥923 ( ≥11.6) |
≥955 ( ≥12) |
342-366(43-46) |
80℃ |
|
N48 |
1380-1420(13.8-14.2) |
≥923( ≥11.6) |
≥955 ( ≥12) |
366-390(46-49) |
80℃ |
|
N50 |
1400-1450(14.0-14.5) |
≥796( ≥10.0) |
≥876( ≥11) |
382-406(48-51) |
60℃ |
|
N52 |
1430-1480(14.3-14.8) |
≥796( ≥10.0) |
≥876 ( ≥11) |
398-422(50-53) |
60℃ |
|
35M |
1170-1220(11.7-12.2) |
≥868( ≥10.9) |
≥1114 ( ≥14) |
263-287(33-36) |
100℃ |
|
38M |
1220-1250(12.2-12.5) |
≥899( ≥11.3) |
≥1114(≥14) |
287-310(36-39) |
100℃ |
|
40M |
1250-1280(12.5-12.8) |
≥923( ≥11.6) |
≥1114 ( ≥14) |
302-326(38-40) |
100℃ |
|
42M |
1280-1320(12.8-13.2) |
≥955(≥12.0) |
≥1114( ≥14) |
318-342(40-43) |
100℃ |
|
45M |
1320-1380(13.2-13.8) |
≥955 ( ≥12.5) |
≥1114( ≥14) |
342-366(43-46) |
100℃ |
|
48M |
1360-1430(13.6-14.3) |
≥1027( ≥12.9) |
≥1114 ( ≥14) |
366-390(46-49) |
100℃ |
|
50M |
1400-1450(14.0-14.5) |
≥1033 ( ≥13.0) |
≥1114 ( ≥14) |
382-406(48-51) |
100℃ |
|
35H |
1170-1220(11.7-12.2) |
≥868( ≥10.9) |
≥1353 ( ≥17) |
263-287(33-36) |
120℃ |
|
38H |
1220-1250(12.2-12.5) |
≥899( ≥11.3) |
≥1353 ( ≥17) |
287-310(36-39) |
120℃ |
|
40H |
1250-1280(12.5-12.8) |
≥923 ( ≥11.6) |
≥1353 ( ≥17) |
302-326(38-41) |
120℃ |
|
42H |
1280-1320(12.8-13.2) |
≥955 ( ≥12.0) |
≥1353 ( ≥17) |
318-342(40-43) |
120℃ |
|
45H |
1300-1360(13.0-13.6) |
≥963 ( ≥12.1) |
≥1353 ( ≥17) |
326-358(43-46) |
120℃ |
|
48H |
1370-1430(13.7-14.3) |
≥955 ( ≥12.5) |
≥1353 ( ≥17) |
366-390(46-49) |
120℃ |
|
30SH |
1080-1130(10.8-11.3) |
≥804 ( ≥10.1) |
≥1592 ( ≥20) |
233-247(28-31) |
150℃ |
|
33SH |
1130-1170(11.3-11.7) |
≥844( ≥10.6) |
≥1592 ( ≥20) |
247-271(31-34) |
150℃ |
|
35SH |
1170-1220(11.7-12.2) |
≥876( ≥11.0) |
≥1592 ( ≥20) |
263-287(33-36) |
150℃ |
|
38SH |
1220-1250(12.2-12.5) |
≥907(≥11.4) |
≥1592 ( ≥20) |
287-310(36-39) |
150℃ |
|
40SH |
1240-1280(12.5-12.8) |
≥939( ≥11.8) |
≥1592 ( ≥20) |
302-326(38-41) |
150℃ |
|
42SH |
1280-1320(12.8-13.2) |
≥987(≥12.4) |
≥1592 ( ≥20) |
318-342(40-43) |
150℃ |
|
45SH |
1320-1380(13.2-13.8) |
≥1003 ( ≥12.6) |
≥1592 ( ≥20) |
342-366(43-46) |
150℃ |
|
30UH |
1080-1130(10.8-11.3) |
≥812 ( ≥10.2) |
≥1990 ( ≥25) |
223-247(28-31) |
180℃ |
|
33UH |
1130-1170(11.3-11.7) |
≥852( ≥10.7) |
≥1990 ( ≥25) |
247-271(31-34) |
180℃ |
|
35UH |
1180-1220(11.8-12.2) |
≥860 ( ≥10.8) |
≥1990 ( ≥25) |
263-287(33-36) |
180℃ |
|
38UH |
1220-1250(12.2-12.5) |
≥876 ( ≥11.0) |
≥1990 ( ≥25) |
287-310(36-39) |
180℃ |
|
40UH |
1240-1280(12.4-12.8) |
≥899 ( ≥11.3) |
≥1990 ( ≥25) |
302-326(38-41) |
180℃ |
|
28EH |
1040-1090(10.4-10.9) |
≥780 ( ≥9.8) |
≥2388 ( ≥30) |
207-231(26-29) |
200℃ |
|
30EH |
1080-1130(10.8-11.3) |
≥812( ≥10.2) |
≥2388( ≥30) |
223-247(28-31) |
200℃ |
|
33EH |
1130-1170(11.3-11.7) |
≥836( ≥10.5) |
≥2388 ( ≥30) |
247-271(31-34) |
200℃ |
|
35EH |
1170-1220(11.7-12.2) |
≥876( ≥11.0) |
≥2388 ( ≥30) |
263-287(33-36) |
200℃ |
|
38EH |
1220-1250(12.2-12.5) |
≥899 ( ≥11.3) |
≥2388( ≥30) |
287-310(36-39) |
200℃ |
|
40EH |
1240-1280(12.4-12.8) |
≥939(≥11.6) |
≥2388 ( ≥30) |
302-326(38-41) |
200℃ |
|
30AH |
1080-1120(10.8-11.2) |
≥804( ≥10.1) |
≥2786( ≥35) |
223-239(28-30) |
220℃ |
|
33AH |
1140-1170(11.4-11.7) |
≥844( ≥10.6) |
≥2786 ( ≥35) |
247-263(31-33) |
220℃ |
|
35AH |
1170-1210(11.7-12.1) |
≥876( ≥10.9) |
≥2786( ≥35) |
263-279(33-35) |
220℃ |
Grades: NdFeB magnets come in various grades, each with its own magnetic properties. These grades are typically denoted by letters such as N, M, H, SH, UH, EH, and AH, followed by a number. The higher the number, the higher the magnetic properties of the magnet. For example, an N52 magnet has higher magnetic properties than an N35 magnet.
|
BH curve |
|
|
|
|
Applications: NdFeB magnets are used in a wide range of applications, including:
1. Electric motors and generators
2. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines
3. Magnetic separators
4. Magnetic bearings
5. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines
6. Loudspeakers and headphones
7. Magnetic therapy devices
8. Magnetic levitation (maglev) systems
9. Sensors and actuators
10. Magnetic couplings
11. Hard disk drives (HDDs) and other data storage devices

Coatings: Raw NdFeB magnets are susceptible to corrosion, so they are typically coated with a protective layer. Common coatings include nickel, zinc, epoxy, or combinations of these materials. The choice of coating depends on factors such as environmental conditions, temperature, and the specific requirements of the application.
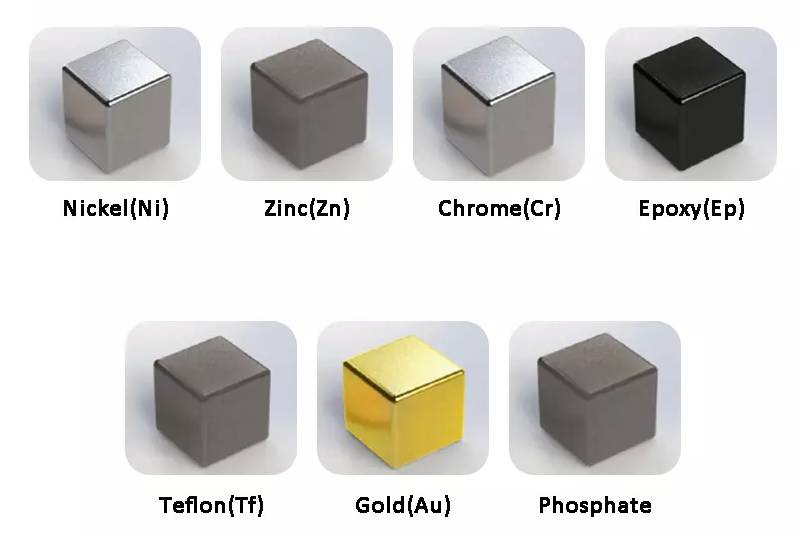
|
Surface |
Coating |
Thickness (Microns) of caoating |
|
镀镍 Nickel |
Ni-Cu-Ni & Ni-Ni |
10-20 um |
|
黑镍 Black Nickel |
Ni-Cu-Ni |
10-20 um |
|
锌Cr6 + Zinc |
Zn |
5-8 um |
|
环保锌 Cr3 + Zinc |
Zn |
5-8 um |
|
锡 Tin |
Ni-Cu-Ni-Sn |
10-25 um |
|
金Gold |
Ni-Cu-Ni-Au |
6-10 um |
|
银Ag |
Ni-Cu-Ni-Ag |
6-10 um |
|
环氧Cpoxy |
Epoxy & Ni-Cu-Epoxy & Zn Epoxy |
10-25 um |
|
钝化 Passivation |
--- |
1-2 um |
|
磷化 Phosphated |
--- |
1-2 um |
Manufacturing Process: NdFeB magnets are typically produced using powder metallurgy techniques, such as sintering or compression bonding. These processes involve compacting powdered neodymium, iron, and boron together under high pressure and then sintering them at high temperatures to form a solid magnet.
1. Mixing 2. Melting 3. Crystallization 4. Milling 5. Pressing 6. Sintering 7. Machining 8. Coating 9. Testing 10. Magnetization 11. Packaging
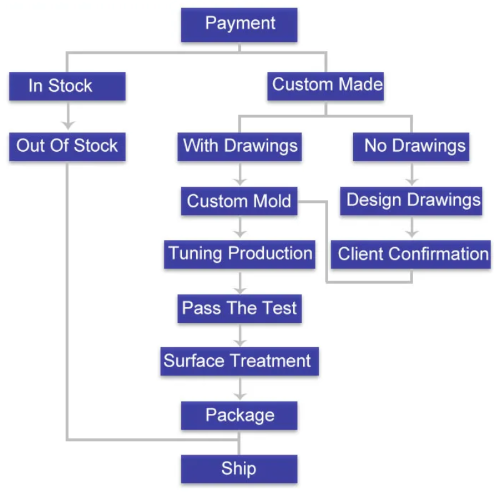
Handling and Safety: NdFeB magnets are extremely powerful and can pose safety risks if mishandled. They can attract ferromagnetic objects from a considerable distance and may cause injury if they pinch or trap body parts between them. Care should be taken when handling NdFeB magnets, especially large or powerful ones, to avoid accidents.
NdFeB magnets are essential components in many modern technologies due to their unmatched combination of high magnetic strength, compact size, and relatively low cost. However, their powerful magnetic fields require careful handling and consideration of safety precautions.